PA (Polyamides) Plastic
What is PA Plastic?
-
Polyamides or Nylon is a major high performance engineering thermoplastics class because of its good balance of properties. Polyamides contain repeating amide linkages i.e. –CO-NH–. It is formed by condensing identical units, copolymers with different units.
-
There are various types of PA plastic are available. Polyamide is easy to work with and guarantees quality.
-
PA plastic has good mechanical properties and this plastic is mainly used in mechanical engineering.
-
PA Plastic is categorised as a technical plastic and is also known as an engineering plastic. Polyamide, more familiarly known as Nylon, is an extremely abrasion-resistant plastic.

Different Types of PA Plastic
-
These are including: Polyamide 6 (PA6), Polyamide 12 (PA12), Polyamide 66 (PA66), Polyamide 69 (PA69), Polyamide 6-10 (PA6-10), Polyamide 6-12 (PA6-12), Polyamide 46 (PA46), Polyamide 1212 (PA1212)
-
Typically, polyamides (or Nylon) are made from polycondensation of diacid with a diamine or by ring-opening polymerization of lactams with 6, 11 or 12 carbon atoms.
-
The monomers may be aliphatic, semi-aromatic or aromatic (aramids).
-
They may be amorphous, semi-crystalline and of greater or lesser crystallinity.
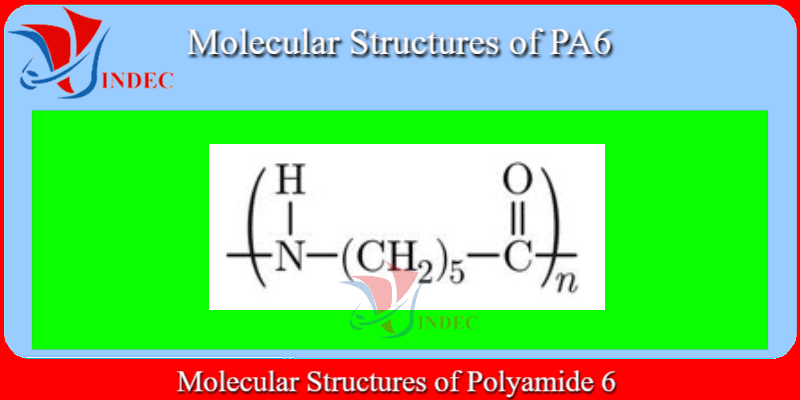
PA6 Plastic - Polyamide 6
-
Polyamide 6 (PA6 Plastic) is also known as Nylon 6 or polycaprolactam. It is one of the most extensively used polyamides globally. It is synthesized by ring-opening polymerization of caprolactam. Melting point of polyamide 6 is 223°C.
-
PA6 Plastic is Caprolactum of Monomer(s)
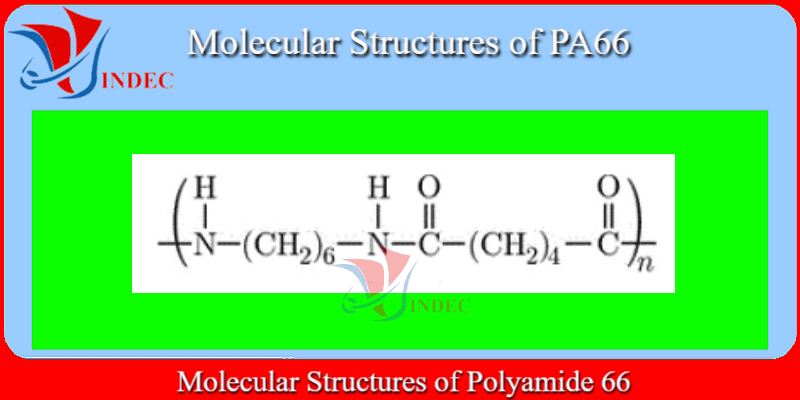
PA66 Plastic - Polyamide 66
-
PA66 Plastic is Hexamethylene Diamine/ Adipic Acid of Monomer(s).
-
Polyamide 66 (PA66) or Nylon 66 is one of the most popular engineering thermoplastics and is majorly used as a replacement to metal in various applications.
-
Nylon 66 is synthesized by polycondensation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid (two monomers each containing 6 carbon atoms). Melting point of polyamide 66 is 255°C.
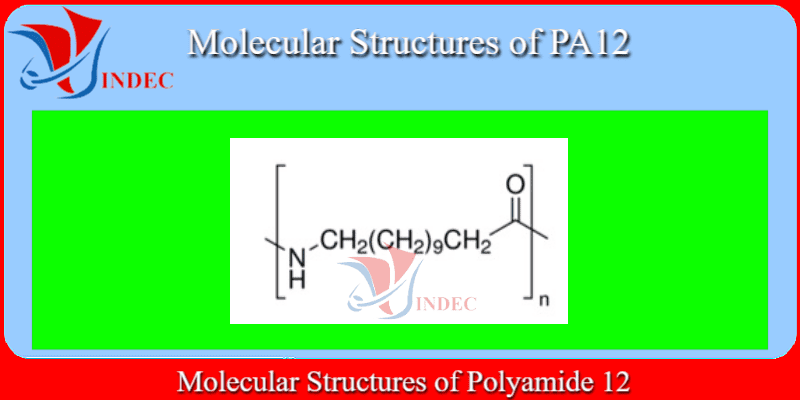
PA12 Plastic - Polyamide 12
-
PA12 Plastic is Laurolactam of Monomer(s)
-
Polyamide 12 (PA12) or Nylon 12 is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic which shows performance similar to Polyamide 11.
-
It can be derived from both petroleum and renewable sources. It is an expensive polymer as compared to other polyamides.
PA69 Plastic - Polyamide 69
-
PA69 Plastic is Hexamethylene Diamine/ Azelaic Acid of Monomer(s)
PA46 Plastic - Polyamide 46
-
PA46 Plastic is 1,4-Diaminobutane/ Adipic Acid
-
Polyamide 46 (PA46) or Nylon 46 is manufactured by polycondensation of adipic acid and 1,4-diaminobutane.
-
Diaminobutane is synthesized from acrylonitrile and HCN.
-
Melting point of polyamide 46 is 295°C.
PA6-10 Plastic - Polyamide 6-10
-
PA6-10 Plastic is Hexamethylene Diamine/ 1,12-Dodecanedioic Acid of Monomer(s)
-
Polyamide 6-10 (PA 6-10) is a semi-crystalline polyamide. PA 6-10 is produced by the polymerization of hexamethylene diamine with a dibasic acid i.e sebacic acid this this case.
-
Melting point of polyamide 6-10 is 223°C.
PA6-12 Plastic - Polyamide 6-12
-
PA6-12 Plastic is Hexamethylene Diamine/ Sebacic Acid of Monomer(s)
PA1212 Plastic - Polyamide 1212
-
PA1212 Plastic is 1,12-Dodecanediamine/ 1,12-Dodecanedioic Acid of Monomer(s)
How Many Types of PA Nylon Plastic
-
These are including: PA Plastic Sheet, PA Plastic Rod, PA Plastic Film
PA Plastic Sheet

PA Plastic Rod

PA Plastic Film
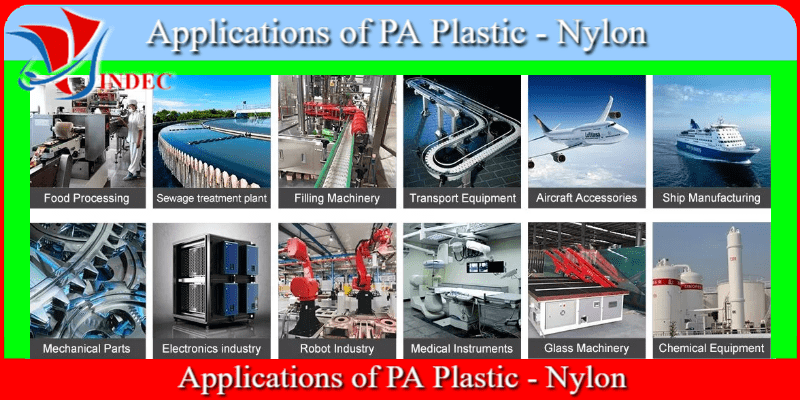
Applications of PA Plastic - Nylon