Piping Equipments
What are Piping Equipments ?
- The various types of piping equipment include gaskets, valves, flanges, actuators, pipes and fittings. The function of these tools are:
All Types of Piping Equipments
• Types of Flanges
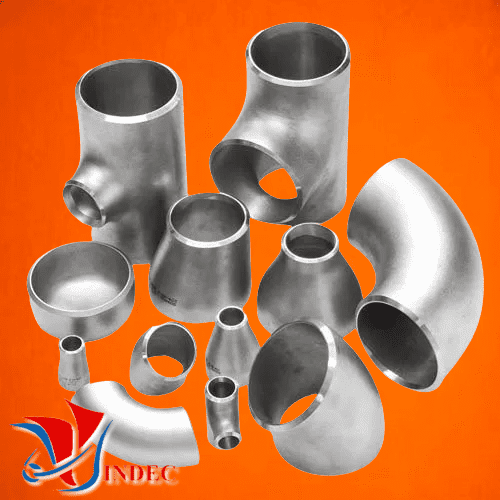
• Types of Butt Welding Fittings
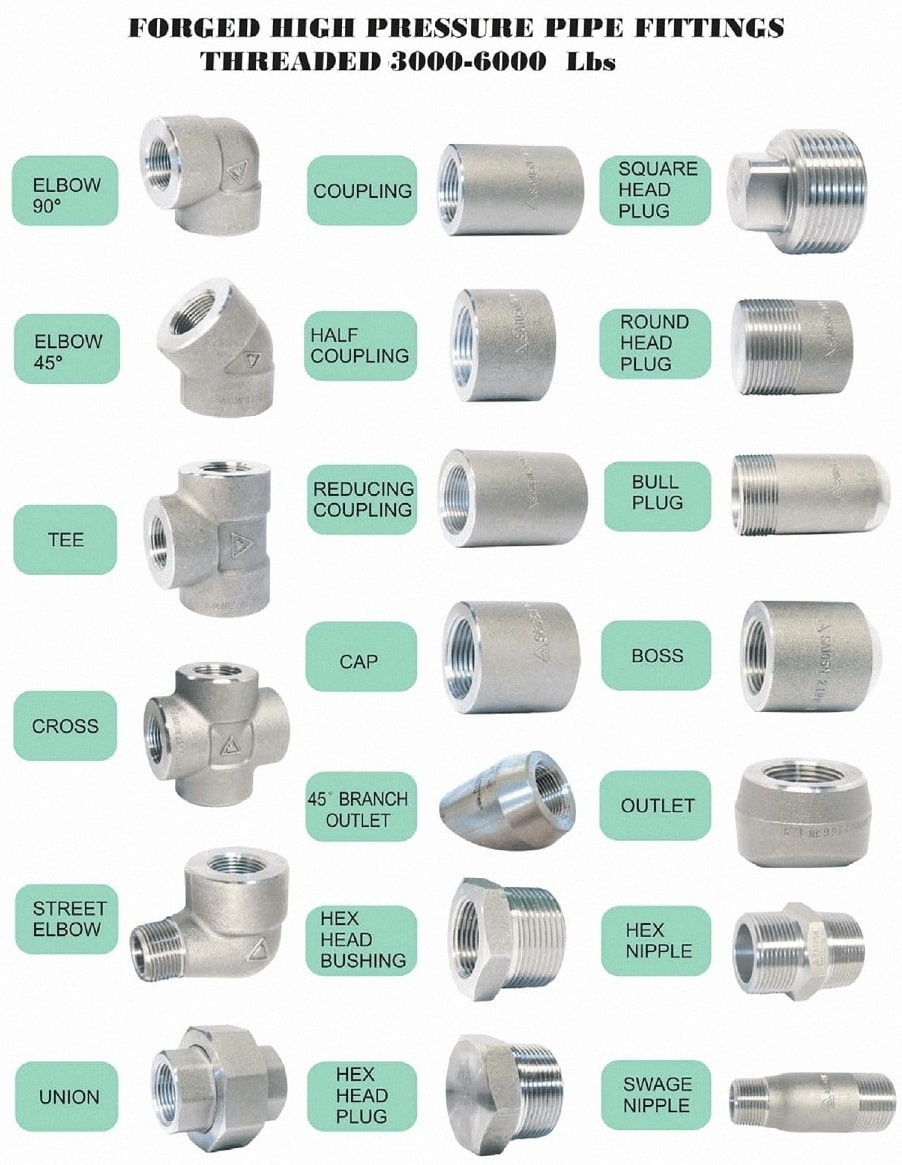
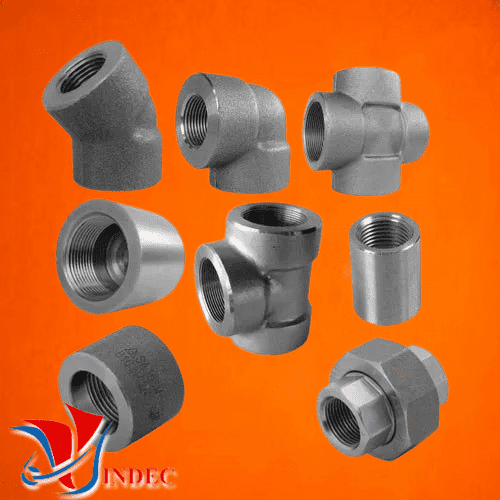
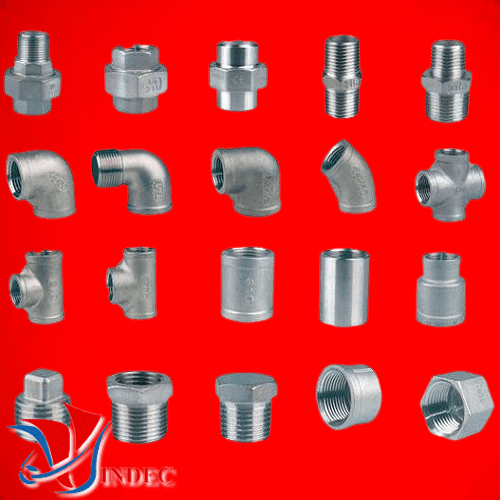
• Types of Threaded Fittings
• Types of Forged Steel Fittings
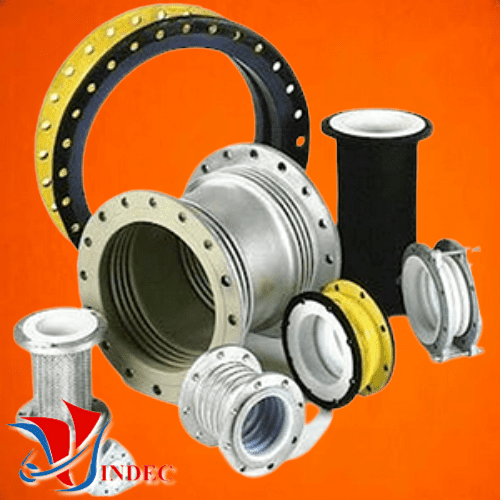
• Types of Expansion Joints
• Types of Bolts - Nuts - Screws
• Types of Galvanized Malleable Iron Fitting
SW&THD fittings